Selecting the appropriate bolt strength is a crucial decision in many engineering, construction, and manufacturing projects. Bolts are responsible for holding together everything from buildings to machinery, and choosing the wrong strength can lead to structural failures, safety hazards, and costly repairs.
In this guide, we will walk you through the key factors to consider when determining the right bolt strength for your application. Additionally, we will provide charts illustrating specifications for different bolt strengths to aid in your decision-making process.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Bolt Strength
Load Requirements:
- The primary consideration when selecting bolt strength is the load or force that the bolt will need to withstand. This load can be static (unchanging) or dynamic (varying with time).
- Calculate the expected load and consider factors like tension, shear, and torque to determine the required bolt strength.
Material Compatibility:
- Ensure that the bolt material is compatible with the materials it will be fastening. Different materials have varying strength requirements.
- Consider factors like corrosion resistance and temperature resistance based on the application's environment.
Safety Factors:
- To account for uncertainties in load estimation and other factors, apply safety factors to the calculated load.
- Common safety factors range from 1.5 to 4, depending on the application's criticality and industry standards.
Bolt Type and Thread Configuration:
- Different bolt types (e.g., hex bolts, carriage bolts) and thread configurations (e.g., fine thread, coarse thread) have varying strength characteristics.
- Choose a bolt type and thread configuration that align with your application's requirements.
Standards and Codes:
- Consult industry-specific standards and building codes for recommended bolt strength specifications.
- Adhering to these standards is often mandatory for ensuring safety and compliance.
Environmental Factors:
- Consider environmental conditions such as temperature fluctuations, moisture exposure, and chemical exposure when selecting bolt materials and coatings.
Bolt Strength Charts
To help you choose the right bolt strength, here is a chart illustrating specifications for different bolt strengths based on their grade or classification:
Table 1: US Standard / Imperial System
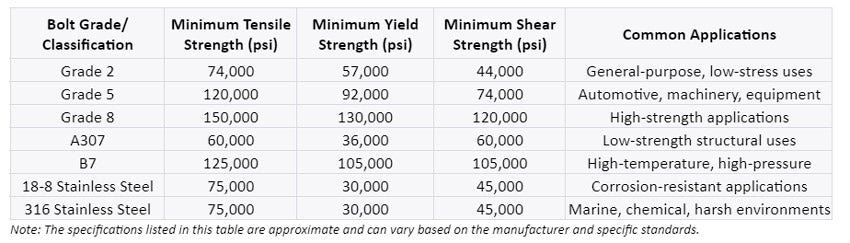
Table 2: Metric System (with US Standard equivalent)
